Which Directory On A Domain Controller Stores Information Such As Group Policies, And Logon Scripts?
Introduction
In this blogpost, we'll discuss about the Group Policies in Active directory, which is i of the of import elements of AD. Nosotros'll encompass concepts like :
- What are Group Policies in Active Directory
- Why Group Policies are required
- What can be accomplised using Group policies
- How group policies can exist enumerated and compromised
Group policies are created to centrally manage the operating organisation, users and computers in the whole Active Directory domain. These policies permit us to manage user and calculator settings from a centralized panel called equally GPMC (Group Policy Management Console).
The shortcut to open Group Policy Management Panel is gpmc.msc
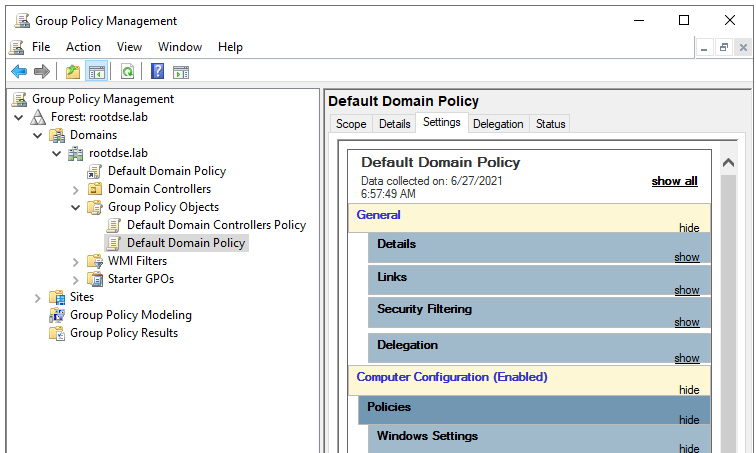
Group Policy Objects
A GPO (Group policy object) contains the Group Policy settings and represents the files related to policy settings in the file system and in the Active Directory. As you lot can run into in the above screenshot, at that place are only two GPOs under Group policy Objects container. These two are the core GPOs which are created automatically when an domain is created.
Default Domain Policy
This default policy defines a set of basic settings for all users and computers in a domain in terms of countersign policy, Kerberos policy and account lockout policy.
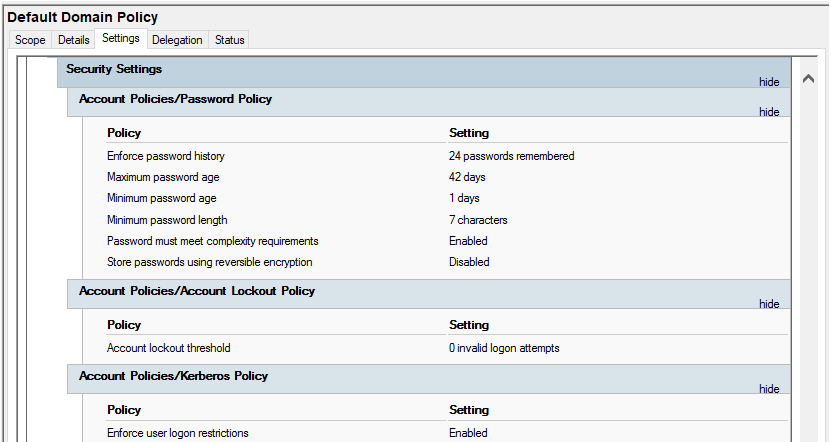
Default Domain Controllers Policy
The Default Domain Controllers Policy defines a fix of basic security and auditing settings for all domain controllers in a domain.

Group policy objects are a prepare of policies that are grouped together and applied to either computer or user objects.

Group Policy Management Editor
The shortcut to open Group Policy Management Editor is gpedit.msc. This is the user interface where you can edit the group policies. As you lot can see in the higher up screenshot, the policy settings are divided into two categories: computer configuration and user configuration.
Computer Configuration
Allow's say if the settings of a GPO is specified under computer configuration, and information technology is applied on a detail computer object, and so that computer object will accept that specified security settings, system behavior, application settings, and calculator startup and shutdown scripts equally specified by the GPO irrespective of the user who logs on to the estimator on which GPO is applied.
User Configuration
In this instance, the policies defined nether user configuration defines the user specific system behavior, awarding settings, security settings, assigned and published applications, user logon and logoff scripts, and folder redirection. If a policy is divers for a particular user, it will be applicable on whatsoever organization where that user logs in.
Note:- The policies defined under the estimator-configuration override the ones which are defined nether user configuration.
Once a GPO is created, it needs to be linked to one or more AD containers, like to the whole domain or some item OU (organizational unit) in order to take outcome. For example, if you want to create a Group Policy to grant all members of DB Admins squad admission to required shared folders for SQL, then this GPO has to be linked to just the DBAdmins OU.
Common GPOs
Some common type of group policies that are used to enable different kind of tasks similar setting up:
- Security policies similar disabling NTLM authentication, and custom policies like restricting access to the command prompt for normal users
- IT policies like restricting access to USB drives, configuring logon imprint to display legal notices to end users etc.
- Policies for audit and compliance like enabling the advanced windows auditing policies to enable audit for important objects and logging the recommended important windows events IDs in the events viewer etc.
- Complex password policies in a domain to bargain with password spraying attacks
- Automation policies like deploying standard tools on multiple computers/servers, mapping network drives, automating logon/logoff tasks and much more than.
Grouping Policy Refresh Interval
There is a refresh interval which defines when the time when a particular domain computer or server requests the grouping policy updates from a domain controller to make sure to replicate the changes in whatsoever of the Grouping policies. The daefault refresh interval is 90 minutes with a random offset interval added to every reckoner/server to prevent all the domain machines from requesting group policy updates from DC at the aforementioned fourth dimension. Volition hash out more about GPOs later on in this series.
SYSVOL
One of the most of import network share in Advertizing is SYSVOL since information technology stores the Grouping policy templates and is shared past default on domain controllers. All the domain computers access this share to check the domain policies. It's default location is %SYSTEMROOT%\SYSVOL\sysvol in the domain controller. And the location on network would be \\<domain_name>\SYSVOL
A sysvol folder is made upwardly of following components:
Scripts (i.eastward. startup scripts and files like .bat, vbs etc. that are referenced in GPOs)
Group Policies folder and templates (replicated throughout the domain)
Junction Points (work like a shortcut. One directory tin can indicate to a dissimilar directory)
SYSVOL Policies folder
The SYSVOL policies binder contains all the GPOs. And folder name for each GPO is same as that GPO's GUID.

Beneath are the components of a Policy binder in SYSVOL.
Machine – (stores GPO'due south machine specific config)
User – (stores GPO's user specific config)
GPT.INI – (stores GPO config)

SYSVOL replication is done past DFSR (Distributed File Organization Replication) which is the default replication mechanism for SYSVOL folder replication domain-broad.
Grouping Policy Preferences
Microsoft introduced an important feature called equally "Group Policy Preferences" which helped to store and use credentials in scenarios like creating scheduled tasks, changing local admin password on all workstations etc. It was really helpful for administrators since it provides an automated mechanism (instead of doing it with the aid of scripts) where the passwords are not saved in cleartext like in case of scripts, but were stored equally AES-256 bit encrypted in the xml file in SYSVOL directory. Only later Microsoft published the private key on their MSDN portal which immune to decrypt any countersign stored in the xml files created like this.

Since everyone has read admission to SYSVOL, it is simply a affair of finding the cpassword in the XML files and decrypting the passwords.
PowerSploit'southward GPP-Password searches xml in sysvol policies directory for cpassword field and decrypts it using the key that Microsoft published earlier.
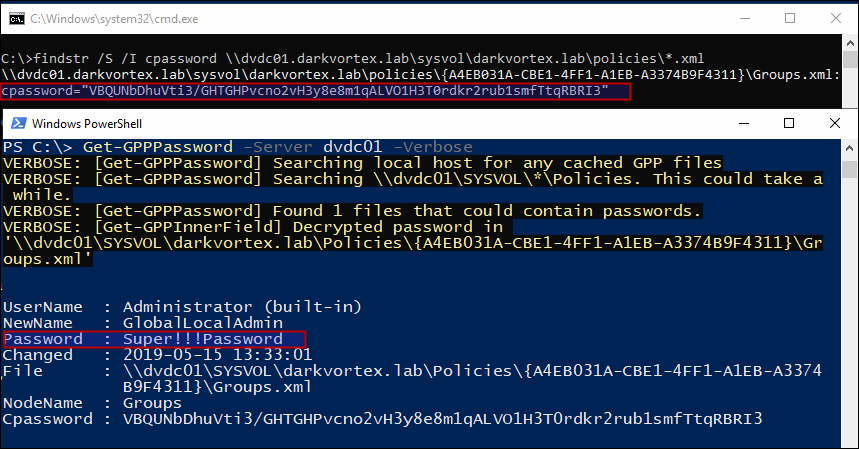
Though Microsoft released a patch after and disabled the choice to enter countersign similar this but the XML files are still there if not removed by admins and a lot of times the countersign works and is a good practise to chase for these files. And and then later Microsoft a way to change local Administrator password by using LAPS (Local Administrator Countersign Solution).
Best practices:
- For system administrators is to delete the existing GPP xml files in the SYSVOL folder which have passwords and make sure in that location are no such files there. And
- For pentesters, the best practice is to enumerate the SYSVOL policies binder to hunt for xml files containing
cpassword. - Best practice for defenders is to create Ad decoys to have xml files with passwords in information technology and enable auditing to get alerts when someone access those folders which are not linked to actual GPOs. I'll write a detailed post on this later in this series.
Finding the GPOs in a Domain
To bank check all the GPOs in a domain, we tin can use below command:
PS C:\> Get-GPO -All | Select DisplayName DisplayName ----------- Remove OneDrive Default Domain Policy Bginfo Default Domain Controllers Policy Remove windows features No car-restart (wupdates) No Sleep
Viewing the Settings of a GPO
To view the settings of a GPO, we can run
PS C:\> Get-GPOReport -Name "<GPO Name>" -Path <Path With File Proper name> -ReportType "<HTML|XML>" 
We can actually see the definition of a policy in xml format, like what is GPO doing if it is enabling a firewall rule or running a script etc:
<Computer> <VersionDirectory>1</VersionDirectory> <VersionSysvol>1</VersionSysvol> <Enabled>true</Enabled> <ExtensionData> <Extension xmlns:q1="http://www.microsoft.com/GroupPolicy/Settings/WindowsFirewall" xsi:type="q1:WindowsFirewallSettings"> <q1:GlobalSettings> <q1:PolicyVersion> <q1:Value>541</q1:Value> </q1:PolicyVersion> </q1:GlobalSettings> <q1:InboundFirewallRules> <q1:Version>2.29</q1:Version> <q1:Activity>Allow</q1:Action> <q1:Name>Allow WinRM port 5985 </q1:Name> <q1:Dir>In</q1:Dir> <q1:LPort>5985</q1:LPort> <q1:Protocol>6</q1:Protocol> <q1:Agile>true</q1:Active> </q1:InboundFirewallRules> </Extension> <Proper name>Windows Firewall</Proper name> </ExtensionData> <ExtensionData> <Extension xmlns:q2="http://www.microsoft.com/GroupPolicy/Settings/Registry" xsi:type="q2:RegistrySettings"> <q2:Blocked>imitation</q2:Blocked> </Extension> <Name>Registry</Name> </ExtensionData> </Computer> <User> <VersionDirectory>1</VersionDirectory> <VersionSysvol>1</VersionSysvol> <Enabled>true</Enabled> </User> </GPO> In the above config, we can run into information technology is enabling a rule in Windows Firewall.
Finding misconfigured Group policies
To demonstrate this, I created a GPO and provided a user ghost permissions to edit the GPO.

At present, we'll get the cn of the GPO "Local Admin Password"

And do an ACL check on this GPO and see the permissions that user ghost has that we configured before.

This is how a misconfigured Group policy object looks like. Since user ghost has the permissions to edit the GPO, the settings tin exist edited and another chore be accomplished from this GPO without domain admin privileges.
Which Directory On A Domain Controller Stores Information Such As Group Policies, And Logon Scripts?,
Source: https://rootdse.org/posts/active-directory-basics-3/
Posted by: essaryhavesiont.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Directory On A Domain Controller Stores Information Such As Group Policies, And Logon Scripts?"
Post a Comment